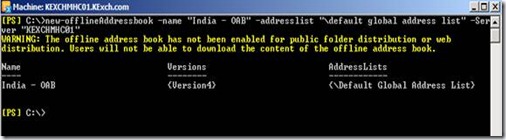
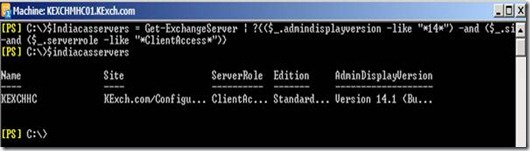
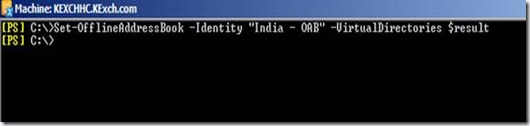
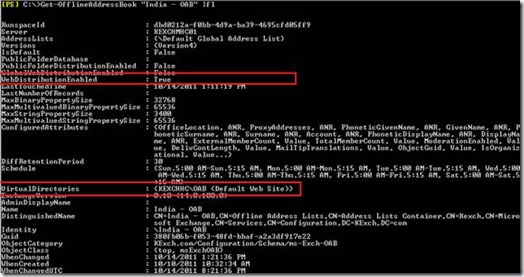
When we say cross forest ad migration then the first thing which comes to the mind is Active Directory Migration Tool. It’s a free and very easy and powerful tool from Microsoft. Doesn’t look very fancy but does its task. There are various tools available in the market to perform cross forest migration but at we will talk about ADMT and its features and how we can use it. Before you work on ADMT in the production, you need to perform through understanding of the ADMT, test it in the lab and then it to the production.
Note: Not performing through testing can be distractive for the users. Users may lose password, lose share access and you will be in trouble.
ADMT features
1. It provide various wizards to migrate User accounts, computers accounts, service accounts, Group
2. Migrate Sid History which helps user to maintain the access to network share, application and other services even after the user been migrated to different forest
3. Migrate password form source forest to target forest.
Red.com Green.com
Current Lab Setup
| Red.com Domain | Green.com Domain |
| Domain controller (windows 2003) | Domain controller(windows 2008) |
| following Software installed in Source domain controller PES 3.1(Password Export Server) | Domain member Server(windows 2003) following Software installed ADMT 3.0(Active directory migration tool) .net Framework version 2.0 SQL 2005 with latest service pack |
Installation of ADMT tool on the Domain member Server
Please follow the below process order to install prerequisites and ADMT. If you have domain member server is windows 2008 or Windows 2008 R2 then you can install the latest version of the ADMT 3.1 or 3.2 respectively. In my lab I have the domain member server as widows 2003 so I am forced to install ADMT 3.0
- Install Microsoft .NET Framework Version 2.0 Redistributable Package (x86)
- Install SQL 2005
- Install Latest SQL service pack
- Install ADMT tool and accept the default database selection (If SQL 2005 is not installed prior to installing ADMT tool then it will automatically install Microsoft SQL Server Desktop Edition)
DNS Configuration between forests
DNS Configuration is a one of the primary requirement to communicate between two forests
DNS can be configured in two ways, either by creating secondary zone or forwarders. Configuring forwarders is much easier then creating secondary zone. Secondary zone has a read-only copy of the particular domain but forwarders are just forward the request to the target domain. Response to the DNS request is much faster in secondary zone than forwarders
Let me show you show to create secondary zone.
- Login to Green.com Domain controller
- Access DNS Manager
- Right click on the forward lookup zone and select New zone and click on Next
Figure 1. Creating new Zone
4. Select Secondary zone and click on Next
Figure 2. Creating new Secondary Zone
5. Provide the target domain name and click on Next
Figure 3. Providing DNS Zone name
6. Provide red.com DNS server IP address and click on Next and click on finish to complete the configuration
Figure 4. Configuring with Master DNS server of red.com
7. Need to follow the above same process (1 to 6) on the red.com DNS server to create the secondary zone for green.com domain
Cross forest trust configuration
1. Connect to the Target domain controller (green.com) and access Active directory domain and trusts from the Administrative tools
2. Right click on Active directory Domain and trusts and click on properties.
Figure 5. Starting with Trust configuration
3. Select the Trust Tab and click on new Trust and select next on welcome screen
Figure 6. Trusts tab to start the new trust configuration between forests
4. Provide the trust name with the source domain red.com and click on next
Figure 7. Domain name which you wanted to trust
5. Select external trust, as you cannot create cross forest trust between AD 2003 and AD 2008 and click on next
Figure 8. Configuring External trust
6. Select “two way” trust and click on next
Figure 9. Selecting Two-way trust option
7. Select the option “both this domain and the specified domain”
Figure 10. Option to select trust on both from red.com and green.com
8. Input the source (red.com) account which has administrative privileges and click on next
Figure 11. Passing account having administrative privileges on red.com
9. Select “Domain-Wide authentication” for red.com and click on next
Figure 12. Selecting Domain-wide authentication on outgoing trust for local domain
10. Domain wide authentication for the local domain and click on next
Figure 13. Selecting Domain-wide authentication on outgoing trust for specified remote domain
11. Select “yes, confirm the outgoing trust”
Figure 14. Confirmation to create outgoing trust
12. Select “Yes, confirm the incoming trust” and next and click on finish the configuration.
Figure 15. Confirmation to create incoming trust
13. Successfully created outgoing and incoming external trust between both the forest
Figure 16. Successful status of external trust creation.
I hope you like this part of the article will soon come up the other parts of the articles.