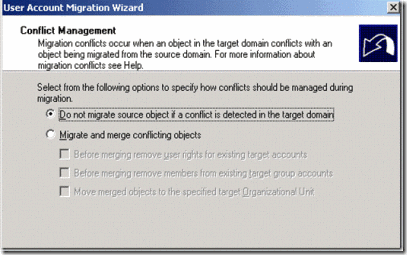
This document is to provide step by step instruction to GAL Sync between Red.com (Exchange 2003) and Blue.com (Exchange 2007 ) organization using IIFP SP2
This document is majorly divided into 4 parts
1. Installing and configuration IIFP
2. Preparing and configuring Active Directory on both Red.com and Blue.com
3. Creating and configuration MA Agents to create mail enabled contacts in both Active directory forest
4. Executing and scheduling MA profiles
Lets talk each of the parts in detail
1. Installing and Configuration IIFP
Follow these steps in order to build and setup IIFP on a Windows Server on any of the domain, either red.com or blue.com
1. Install Windows 2003 R2 enterprise edition and configure server as per best practice
2. Join the server to the domain
3. Install IIS, ASP.net 2.0
4. Install Microsoft SQL Server 2005 with SP1
5. Install Identity Integration Feature Pack SP2
6. Run Microsoft Updates to bring system up to latest patch levels.
2. Creating and Configuring Blue.com – GAL MA
2.1 Configuring Red.com Active Director
1. Login to Red.com domain controller
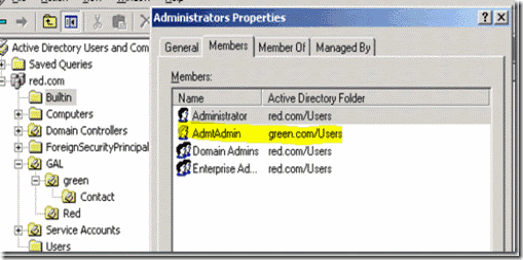
2. From Start, click Administrative Tools; click Active Directory Users and Computers.
3. Select View from the top drop down menu and select Advanced Features.
4. Create new user “RedGalsync” with password and ensure that password is set not to expire and not to change the password for next logon
5. Select RED.COM and right-click, select Delegate Control
6. On the Welcome to the Delegation of Control Wizard page click Next.
7. On the Users or Groups page click Add.
8. On the Select Users, Computers, or Groups dialog box type “RedGalsync” and click OK.
9. On the Users or Groups page click Next.
10. On the Tasks to Delegate page select create a custom task to delegate, and click Next.
11. On the Active Directory Object Type page except the defaults and click Next.
12. On the Permissions page select General, Property-specific, and Creation/deletion of specific child objects, under permissions select Replicate Directory Changes and Replication Synchronization, and click Next.
13. On the Completing to the Delegation of Control Wizard page click Finish.
14. Create new OU with the name “Blue” under root and create sub OU “Contacts”
15. Right-click the Contacts OU and select Properties.
16. On the Contacts Properties dialog box click Security.
17. On the Contacts Properties dialog box click Add.
18. On the Select Users, Computers, or Groups dialog box type “REDGalsync” and click OK.
19. On the Contacts Properties dialog box select Read, Write, Create All Child Objects, and Delete All Child Objects, and then click OK. Make sure to Apply to this child and all objects.
20. Open ADSIEdit and navigate to the container “Blue”
21. Right-click on OU “Contacts” and select Properties.
22. Click on the Security tab, and click Advanced.
23. Choose to Add an ACE.
24. Specify REDGalsync to apply the permissions to. This will display the permissions dialog.
25. Click on Properties.
26. Drop down the Apply Onto dropdown box and select Child Objects Only.
27. Scroll down and mark Write proxyAddresses – Allow.
28. Choose to save the properties. This permission will be applied to every child object whose Allow inheritable permissions from the parent to propagate to this object and all child objects option is selected. This is located in the user’s Advanced Security property sheet. Any user that does not have this selected will not have the permissions granted to it
2.2 Configuring Blue.com Active Director
1. Login to Blue.com domain controller
2. From Start, click Administrative Tools; click Active Directory Users and Computers.
3. Select View from the top drop down menu and select Advanced Features.
4. Create new user “BlueGalsync” with password and ensure that password is set not to expire and not to change the password for next logon
5. Select Blue.com and right-click, select Delegate Control
6. On the Welcome to the Delegation of Control Wizard page click Next.
7. On the Users or Groups page click Add.
8. On the Select Users, Computers, or Groups dialog box type “BlueGalsync” and click OK.
9. On the Users or Groups page click Next.
10. On the Tasks to Delegate page select create a custom task to delegate, and click Next.
11. On the Active Directory Object Type page except the defaults and click Next.
12. On the Permissions page select General, Property-specific, and Creation/deletion of specific child objects, under permissions select Replicate Directory Changes and Replication Synchronization, and click Next.
13. On the Completing to the Delegation of Control Wizard page click Finish.
14. Create new OU with the name “Red” under root and create sub OU “Contacts”
15. Right-click the Contacts OU and select Properties.
16. On the Contacts Properties dialog box click Security.
17. On the Contacts Properties dialog box click Add.
18. On the Select Users, Computers, or Groups dialog box type BlueGalsync and click OK.
19. On the Contacts Properties dialog box select Read, Write, Create All Child Objects, and Delete All Child Objects, and then click OK. Make sure to Apply to this child and all objects.
20. Open ADSIEdit and navigate to the container name “Red”
21. Right-click on OU “Contacts” and select Properties.
22. Click on the Security tab, and click Advanced.
23. Choose to Add an ACE.
24. Specify BlueGalsync to apply the permissions to. This will display the permissions dialog.
25. Click on Properties.
26. Drop down the Apply Onto dropdown box and select Child Objects Only.
27. Scroll down and mark Write proxyAddresses – Allow.
28. Choose to save the properties. This permission will be applied to every child object whose Allow inheritable permissions from the parent to propagate to this object and all child objects option is selected. This is located in the user’s Advanced Security property sheet. Any user that does not have this selected will not have the permissions granted to it